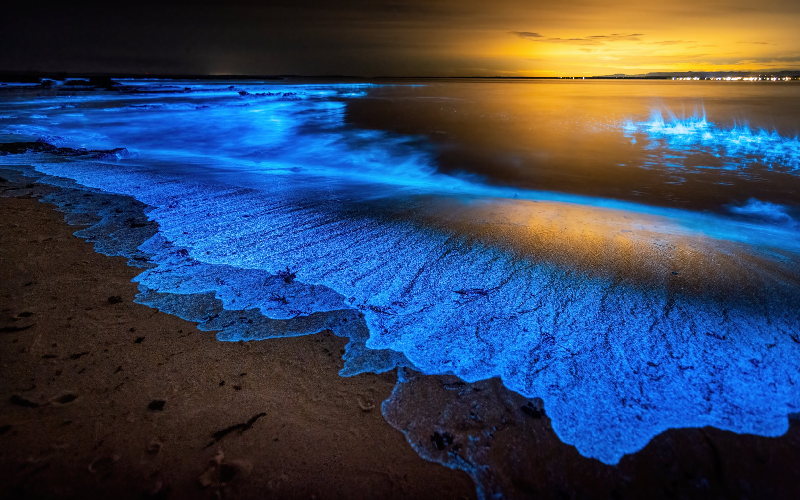
Bioluminescent algae are tiny marine organisms that emit an otherworldly glow in the dark. Although this can occur in any ocean location or depth, some of the most breathtaking displays happen near the shore when the algae are stirred by the movement of waves or boats, producing a sparkling effect.
What Is Bioluminescence?
Bioluminescence is a phenomenon that occurs in many species of living organisms, including bacteria, fungi, and animals. In these organisms, light is produced through chemical reactions within specialized cells called photocytes. The light produced can be used for various purposes, such as attracting mates, deterring predators, or luring prey.
Bioluminescence can vary in intensity and color, with the most common color being green or blue. The exact mechanism by which the light is produced and the specific chemicals involved can vary between species.
In marine environments, bioluminescence is commonly seen in jellyfish, squid, and many types of algae. On land, bioluminescent fungi can be found in some forests, and fireflies are well-known for their bioluminescent flashes.
Bioluminescence has inspired numerous scientific and technological advances. For example, the study of bioluminescent organisms has led to a deeper understanding of cellular processes and has provided valuable information for the development of new medical treatments. Additionally, bioluminescent compounds and materials have been used in various fields, such as biotechnology and environmental monitoring.
The Causes of Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is caused by chemical reactions within specialized cells called photocytes. The exact mechanisms by which the light is produced and the specific chemicals involved can vary between species, but in general, bioluminescence is produced through the oxidation of a molecule called luciferin, which releases energy in the form of light.
In some species, such as jellyfish and fireflies, bioluminescence is controlled by enzymes, which regulate the chemical reactions that produce light. Other species, such as certain types of algae, produce light continuously in response to stimuli, such as movement or changes in the environment.
In some cases, bioluminescence is also influenced by external factors, such as changes in temperature, pressure, or light levels. The ability to control bioluminescence has evolved in many species for various purposes, such as communication, camouflage, and defense against predators.

Bioluminescent Benefits to Humans
Bioluminescence has a number of potential benefits for humans. It has the potential to provide numerous benefits for humans, and ongoing research is exploring new ways to harness this fascinating phenomenon for the betterment of society. Some of these benefits include:
Medical Applications
Bioluminescent compounds have been used in medical imaging and diagnostics, allowing doctors to visualize the distribution and activity of drugs and other biological markers in the body. Bioluminescence has a number of potential medical applications that can benefit humans, including:
- Medical Imaging: Bioluminescent compounds can be used to visualize the distribution and activity of drugs and other biological markers within the body. This can help doctors to diagnose diseases, monitor the effectiveness of treatments, and plan surgical procedures.
- Diagnostics: Bioluminescent assays can be used to detect the presence of disease markers, such as bacteria or viruses, in a quick, non-invasive manner. This can help to diagnose infections and other conditions more effectively and with greater speed.
- Drug Development: Bioluminescent organisms and their light-producing compounds have been used to test the effectiveness of potential new drugs and to monitor their interactions with living systems.
- Cell Biology: Bioluminescence can be used to study cellular processes and to understand how cells function and interact with their environment.
- Tumor Detection: Bioluminescent compounds can be used to visualize the growth of tumors in real-time, helping doctors to monitor the effectiveness of treatments and make more informed decisions about patient care.
Biotechnology
Bioluminescent organisms and their light-producing compounds have been used in various biotechnology applications, including the development of assays for drug discovery and the study of cellular processes. Bioluminescence has a number of potential biotechnology applications that can benefit humans, including:
- Assays: Bioluminescent assays have been developed to study a wide range of biological processes, from the detection of toxins to the measurement of gene expression. These assays can provide quick, sensitive, and non-invasive methods for analyzing biological samples.
- Drug Discovery: Bioluminescent organisms and their light-producing compounds have been used to screen for new drugs and to test the efficacy of existing drugs. This can help to speed up the drug discovery process and to identify new treatments for a wide range of conditions.
- Genetic Engineering: Bioluminescence can be used to study gene expression and regulation, allowing scientists to understand how different genes control cellular processes and to develop new genetic engineering techniques.
- Bioreporters: Bioluminescent organisms can be used as bioreporters, providing real-time information about the presence and activity of pollutants, toxic compounds, and other environmental factors.
- Cell Culture: Bioluminescent cells and tissues have been used as in vitro model systems, providing a convenient and easily monitored platform for the study of cellular processes and the testing of new drugs.
Environmental Monitoring
Bioluminescent algae and other organisms have been used as indicators of environmental conditions, such as water quality, temperature, and pollutants. Bioluminescence has a number of potential benefits for environmental monitoring, including:
- Water Quality: Bioluminescent algae and other organisms have been used as indicators of water quality, providing a rapid and non-invasive method for monitoring environmental conditions.
- Pollutants: Bioluminescent bioreporters can be used to monitor the presence and activity of pollutants in the environment, such as heavy metals, oil spills, and toxic compounds.
- Climate Change: Bioluminescent organisms can be used as indicators of environmental change, providing information about water temperature, acidity, and other important parameters.
- Habitat Monitoring: Bioluminescent organisms can be used to monitor the health and diversity of ecosystems, providing important information about the impacts of human activities on the environment.
- Biodiversity: Bioluminescent organisms are an important component of marine and terrestrial ecosystems, and their distribution and abundance can provide valuable insights into the diversity and health of these systems.

Lighting
Bioluminescent materials have been developed for use in lighting applications, offering a potentially sustainable alternative to traditional lighting sources. Bioluminescence has potential benefits for lighting, including:
- Energy Efficiency: Bioluminescent lights use less energy than traditional artificial lighting and can provide a sustainable alternative to conventional lighting sources.
- Flexibility: Bioluminescent lights can be easily adapted to different environments and applications, providing a flexible lighting solution for a wide range of settings.
- Cost Effective: Bioluminescent lights can be less expensive to produce and maintain compared to traditional artificial lights, making them an attractive option for many applications.
- Eco-Friendly: Bioluminescent lights produce no harmful emissions and do not contribute to light pollution, making them a more environmentally friendly option compared to traditional artificial lights.
- Unique Aesthetics: Bioluminescent lights can create unique and visually stunning lighting effects, adding an element of beauty and creativity to a wide range of applications.
Aesthetic Value
The stunning displays of bioluminescent organisms in the natural world can provide aesthetic enjoyment and inspire wonder and awe in people of all ages. Bioluminescence has a number of potential benefits for aesthetic value, including:
- Beauty: Bioluminescent organisms and their ethereal glow can provide a visually stunning and captivating experience, especially in the dark.
- Inspiration: Bioluminescence has inspired artists, designers, and architects, leading to the creation of unique and imaginative works of art and design.
- Creativity: Bioluminescence can be used in a variety of creative applications, from illuminating pathways and gardens to creating interactive installations and performances.
- Education: Bioluminescence can be used to educate and inform the public about science, biology, and the natural world, providing an engaging and memorable experience.
- Spirituality: Bioluminescent organisms can have spiritual and cultural significance, with some cultures considering them as symbols of life, renewal, and hope.
Environmental Impact of Bioluminescent Algae
Bioluminescent algae can have both positive and negative impacts on the environment. On the one hand, they can play a role in the food chain and provide a source of food for other marine organisms. They can also help to maintain the balance of marine ecosystems by consuming waste materials and producing oxygen through photosynthesis.
However, bioluminescent algae can also have negative impacts on the environment. In some cases, blooms of bioluminescent algae can occur, causing significant disruptions to local marine ecosystems. These blooms can reduce the amount of light that reaches deeper water levels, affecting the growth and behavior of other marine organisms.
Bioluminescent algae can also produce toxic compounds that can harm other marine species and potentially impact human health if consumed. Additionally, the increase in nutrients in the water caused by bioluminescent blooms can lead to the overgrowth of other types of harmful algae, which can produce even more toxins.
Overall, the impact of bioluminescent algae on the environment depends on the specific species and the environmental conditions in which they are found. Further research is needed to fully understand the potential impacts of these organisms on the marine environment and to develop effective strategies for managing and mitigating any negative effects.

